Wire-mesh Sensors
Wire-mesh sensors measure the instantaneous, local fluid conductivity on a matrix of up to 128 x 128 measurement locations, with a frame-rate of up to 10,000 frames/s.
A simplified scheme of the wire-mesh working principle together with an example of a wire-mesh sensor for a 2″ pipe is shown below:

Simplified scheme of the wire-mesh working principle together with an example of a wire-mesh sensor for a 2″ pipe
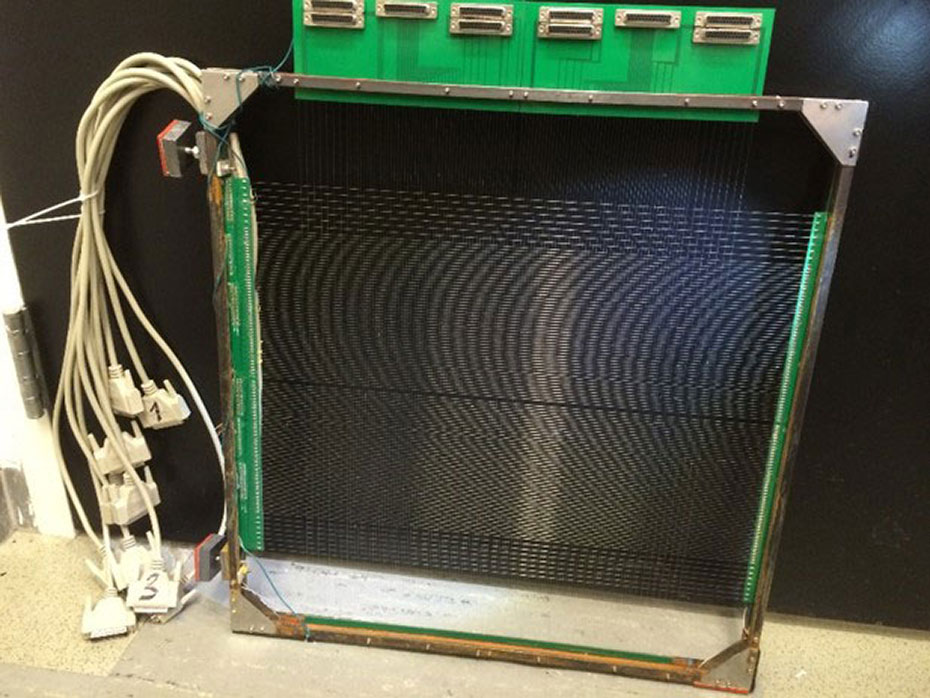

Larger wire-mesh sensor for a square cross-section
A larger wire-mesh sensor for a square cross-section is shown on the left. We design and build sensors for a variety of cross-sections.
Examples of measurements taken with wiremesh sensors for single-phase mixing flows and two-phase flow respectively are shown in the two videos below:
3D measurement of transient flashing flow using two wire-mesh sensors.
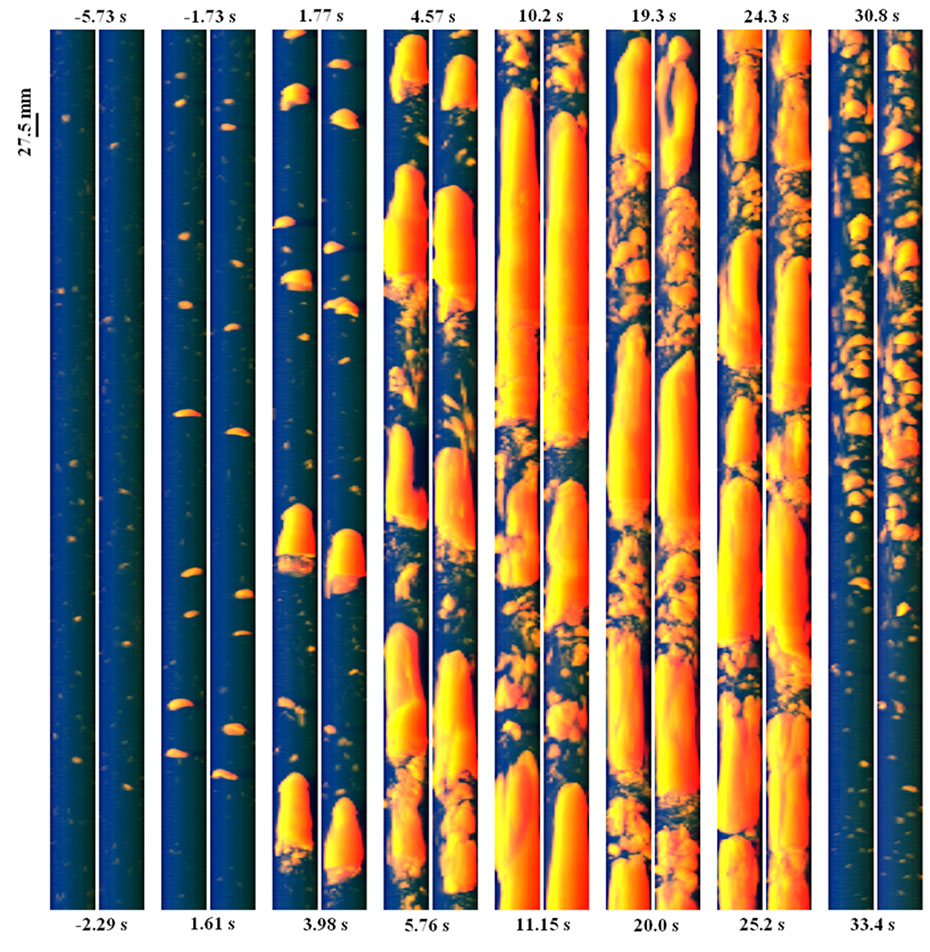
Experimental data on flashing flow